|
BEM++
2.0
|
|
BEM++
2.0
|
New-style options controlling quadrature accuracy. More...
#include </home/wojtek/Projects/BEM/bempp-sven/bempp/lib/fiber/accuracy_options.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| AccuracyOptionsEx () | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| AccuracyOptionsEx (const AccuracyOptions &oldStyleOpts) | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| const QuadratureOptions & | singleRegular () const |
| Return the options controlling integration of regular functions on single elements. | |
| const QuadratureOptions & | singleRegular (double normalizedDistance) const |
| Return the options controlling integration, on single elements, of functions that have singularities outside these elements. More... | |
| void | setSingleRegular (int accuracyOrder, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements. More... | |
| void | setSingleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, int accuracyOrder2, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements. More... | |
| void | setSingleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, double maxNormalizedDistance2, int accuracyOrder2, int accuracyOrder3, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements. More... | |
| void | setSingleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, double maxNormalizedDistance2, int accuracyOrder2, double maxNormalizedDistance3, int accuracyOrder3, int accuracyOrder4, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements. More... | |
| void | setSingleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, double maxNormalizedDistance2, int accuracyOrder2, double maxNormalizedDistance3, int accuracyOrder3, double maxNormalizedDistance4, int accuracyOrder4, int accuracyOrder5, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements. More... | |
| void | setSingleRegular (const std::vector< double > &maxNormalizedDistances, const std::vector< int > &accuracyOrders, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| const QuadratureOptions & | doubleRegular (double normalizedDistance) const |
| Return the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements. More... | |
| void | setDoubleRegular (int accuracyOrder, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements. More... | |
| void | setDoubleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, int accuracyOrder2, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements. More... | |
| void | setDoubleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, double maxNormalizedDistance2, int accuracyOrder2, int accuracyOrder3, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements. More... | |
| void | setDoubleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, double maxNormalizedDistance2, int accuracyOrder2, double maxNormalizedDistance3, int accuracyOrder3, int accuracyOrder4, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements. More... | |
| void | setDoubleRegular (double maxNormalizedDistance1, int accuracyOrder1, double maxNormalizedDistance2, int accuracyOrder2, double maxNormalizedDistance3, int accuracyOrder3, double maxNormalizedDistance4, int accuracyOrder4, int accuracyOrder5, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements. More... | |
| void | setDoubleRegular (const std::vector< double > &maxNormalizedDistances, const std::vector< int > &accuracyOrders, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| const QuadratureOptions & | doubleSingular () const |
| Return the options controlling integration of singular functions on pairs of elements. | |
| void | setDoubleSingular (int accuracyOrder, bool relativeToDefault=true) |
| Set the options controlling integration of singular functions on pairs of elements. More... | |
New-style options controlling quadrature accuracy.
| Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::AccuracyOptionsEx | ( | ) |
Constructor.
Create an AccuracyOptionsEx object representing default quadrature accuracy settings.
| Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::AccuracyOptionsEx | ( | const AccuracyOptions & | oldStyleOpts | ) |
Constructor.
Convert an old-style AccuracyOptions object to an equivalent new-style AccuracyOptionsEx object.
References Fiber::AccuracyOptions::doubleRegular, Fiber::AccuracyOptions::doubleSingular, and Fiber::AccuracyOptions::singleRegular.
| const QuadratureOptions & Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::doubleRegular | ( | double | normalizedDistance | ) | const |
Return the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements.
The quadrature rule used to approximate this class of integrals may depend on the distance between the two the elements. To retrieve the quadrature rule that should be used to integrate a function defined on a given pair of elements, set normalizedDistance to the distance between the centres of the elements divided by the size of the larger of the two elements.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setDoubleRegular | ( | int | accuracyOrder, |
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements.
Use this overload of setDoubleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of regular functions on pairs of elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be set to accuracyOrder, regardless of the distance between the two elements.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setDoubleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements.
Use this overload of setDoubleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of regular functions on pairs of elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the normalized distance d of the two elements:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1 to accuracyOrder2.
to accuracyOrder2.The normalized distance d is the distance between the centres of the two elements divided by the size of the larger of the elements.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setDoubleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder3, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements.
Use this overload of setDoubleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of regular functions on pairs of elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the normalized distance d of the two elements:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1maxNormalizedDistance2:  to accuracyOrder2
to accuracyOrder2 to accuracyOrder3.
to accuracyOrder3.The normalized distance d is the distance between the centres of the two elements divided by the size of the larger of the elements.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setDoubleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance3, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder3, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder4, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements.
Use this overload of setDoubleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of regular functions on pairs of elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the normalized distance d of the two elements:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1maxNormalizedDistance2:  to accuracyOrder2
to accuracyOrder2maxNormalizedDistance3:  to accuracyOrder3
to accuracyOrder3 to accuracyOrder4.
to accuracyOrder4.The normalized distance d is the distance between the centres of the two elements divided by the size of the larger of the elements.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setDoubleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance3, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder3, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance4, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder4, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder5, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of regular functions on pairs of elements.
Use this overload of setDoubleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of regular functions on pairs of elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the normalized distance d of the two elements:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1maxNormalizedDistance2:  to accuracyOrder2
to accuracyOrder2maxNormalizedDistance3:  to accuracyOrder3
to accuracyOrder3maxNormalizedDistance4:  to accuracyOrder4
to accuracyOrder4 to accuracyOrder5.
to accuracyOrder5.The normalized distance d is the distance between the centres of the two elements divided by the size of the larger of the elements.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setDoubleSingular | ( | int | accuracyOrder, |
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of singular functions on pairs of elements.
If relativeToDefault is set to false, accuracyOrder denotes the desired order of accuracy of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of singular functions on pairs of elements. Otherwise, accuracyOrder denotes the desired increase of the order of accuracy above the default level.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setSingleRegular | ( | int | accuracyOrder, |
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements.
Use this overload of setSingleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of functions on single elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be set to accuracyOrder, regardless of whether the integrated function has a singularity near the element or not.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setSingleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements.
Use this overload of setSingleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of functions on single elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the estimated normalized distance d of the element to the nearest singularity of the function being integrated:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1 to accuracyOrder2.
to accuracyOrder2.The normalized distance d is defined in the documentation of the singleRegular() method.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setSingleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder3, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements.
Use this overload of setSingleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of functions on single elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the estimated normalized distance d of the element to the nearest singularity of the function being integrated:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1maxNormalizedDistance2:  to accuracyOrder2
to accuracyOrder2 to accuracyOrder3.
to accuracyOrder3.The normalized distance d is defined in the documentation of the singleRegular() method.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setSingleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance3, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder3, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder4, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements.
Use this overload of setSingleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of functions on single elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the estimated normalized distance d of the element to the nearest singularity of the function being integrated:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1maxNormalizedDistance2:  to accuracyOrder2
to accuracyOrder2maxNormalizedDistance3:  to accuracyOrder3
to accuracyOrder3 to accuracyOrder4.
to accuracyOrder4.The normalized distance d is defined in the documentation of the singleRegular() method.
| void Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::setSingleRegular | ( | double | maxNormalizedDistance1, |
| int | accuracyOrder1, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance2, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder2, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance3, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder3, | ||
| double | maxNormalizedDistance4, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder4, | ||
| int | accuracyOrder5, | ||
| bool | relativeToDefault = true |
||
| ) |
Set the options controlling integration of functions on single elements.
Use this overload of setSingleRegular() to specify that the order of accuracy o of the quadrature rule used to approximate integrals of functions on single elements (or its increase  over the default level if
over the default level if relativeToDefault is set to true) should be chosen as follows, depending on the estimated normalized distance d of the element to the nearest singularity of the function being integrated:
maxNormalizedDistance1:  to accuracyOrder1
to accuracyOrder1maxNormalizedDistance2:  to accuracyOrder2
to accuracyOrder2maxNormalizedDistance3:  to accuracyOrder3
to accuracyOrder3maxNormalizedDistance4:  to accuracyOrder4
to accuracyOrder4 to accuracyOrder5.
to accuracyOrder5.The normalized distance d is defined in the documentation of the singleRegular() method.
| const QuadratureOptions & Fiber::AccuracyOptionsEx::singleRegular | ( | double | normalizedDistance | ) | const |
Return the options controlling integration, on single elements, of functions that have singularities outside these elements.
This function is called, in particular, to determine the quadrature order used in the approximation of integrals of the form
![\[ \int_E G(x, y) f(y) \, \mathrm{d}(y), \]](form_194.png)
where 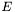 is an element,
is an element, 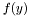 a regular function and
a regular function and 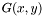 a function singular at
a function singular at 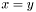 . The
. The normalizedDistance argument should be set to an estimate of the minimum distance between the point 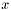 and the element
and the element 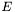 , divided by the size of
, divided by the size of 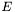 i.e.
i.e. 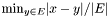 .
.
 1.8.5
1.8.5