|
BEM++
2.0
|
|
BEM++
2.0
|
Classes | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dAdjointDoubleLayerPotentialKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Adjoint double-layer-potential kernel functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dAdjointDoubleLayerPotentialKernelInterpolatedFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Adjoint double-layer-potential kernel functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dDoubleLayerPotentialKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Double-layer-potential kernel functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dDoubleLayerPotentialKernelInterpolatedFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Double-layer-potential kernel functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dFarFieldDoubleLayerPotentialKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Kernel functor used to calculate part of the far-field pattern of a radiating solution of the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dFarFieldSingleLayerPotentialKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Kernel functor used to calculate part of the far-field pattern of a radiating solution of the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dHypersingularKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Hypersingular kernel collection functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dHypersingularKernelInterpolatedFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Hypersingular kernel collection functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dHypersingularOffDiagonalInterpolatedKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Kernel functor for the hypersingular operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D, applicable for test and trial points lying on nonadjacent elements. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dHypersingularOffDiagonalKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Kernel functor for the hypersingular operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D, applicable for test and trial points lying on nonadjacent elements. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dSingleLayerPotentialKernelFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Single-layer-potential kernel functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| class | Fiber::ModifiedHelmholtz3dSingleLayerPotentialKernelInterpolatedFunctor< ValueType_ > |
| Single-layer-potential kernel functor for the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
Functions | |
| template<typename BasisFunctionType , typename KernelType , typename ResultType > | |
| BoundaryOperator < BasisFunctionType, ResultType > | Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dAdjointDoubleLayerBoundaryOperator (const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > &context, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &domain, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &range, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &dualToRange, KernelType waveNumber, const std::string &label="", int symmetry=NO_SYMMETRY, bool useInterpolation=false, int interpPtsPerWavelength=DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY) |
| Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the adjoint double-layer boundary operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| template<typename BasisFunctionType , typename KernelType , typename ResultType > | |
| BoundaryOperator < BasisFunctionType, ResultType > | Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dDoubleLayerBoundaryOperator (const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > &context, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &domain, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &range, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &dualToRange, KernelType waveNumber, const std::string &label="", int symmetry=NO_SYMMETRY, bool useInterpolation=false, int interpPtsPerWavelength=DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY) |
| Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the double-layer boundary operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| template<typename BasisFunctionType , typename KernelType , typename ResultType > | |
| BoundaryOperator < BasisFunctionType, ResultType > | Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dHypersingularBoundaryOperator (const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > &context, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &domain, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &range, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &dualToRange, KernelType waveNumber, const std::string &label="", int symmetry=NO_SYMMETRY, bool useInterpolation=false, int interpPtsPerWavelength=DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY) |
| Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the hypersingular operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
| template<typename BasisFunctionType , typename KernelType , typename ResultType > | |
| BoundaryOperator < BasisFunctionType, ResultType > | Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dSingleLayerBoundaryOperator (const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > &context, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &domain, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &range, const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > &dualToRange, KernelType waveNumber, const std::string &label="", int symmetry=NO_SYMMETRY, bool useInterpolation=false, int interpPtsPerWavelength=DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY) |
| Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the single-layer boundary operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D. More... | |
This submodule contains classes implementing kernels, boundary operators and potential operators related to the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D,
![\[ \biggl(\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2} + \frac{\partial^2}{\partial z^2} - k^2\biggr) u(x, y, z) = 0. \]](form_166.png)
The number 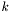 is referred to as the wave number.
is referred to as the wave number.
| BoundaryOperator< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dAdjointDoubleLayerBoundaryOperator | ( | const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > & | context, |
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | domain, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | range, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | dualToRange, | ||
| KernelType | waveNumber, | ||
| const std::string & | label = "", |
||
| int | symmetry = NO_SYMMETRY, |
||
| bool | useInterpolation = false, |
||
| int | interpPtsPerWavelength = DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY |
||
| ) |
Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the adjoint double-layer boundary operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D.
| [in] | context | A Context object that will be used to build the weak form of the boundary operator when necessary. |
| [in] | domain | Function space being the domain of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | range | Function space being the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | dualToRange | Function space dual to the the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | waveNumber | Wave number. See Modified Helmholtz equation in 3D for its definition. |
| [in] | label | Textual label of the operator. If empty, a unique label is generated automatically. |
| [in] | symmetry | Symmetry of the weak form of the operator. Can be any combination of the flags defined in the enumeration type Symmetry. |
| [in] | useInterpolation | If set to false (default), the standard exp() function will be used to evaluate the exponential factor occurring in the kernel. If set to true, the exponential factor will be evaluated by piecewise-cubic interpolation of values calculated in advance on a regular grid. This normally speeds up calculations, but might result in a loss of accuracy. This is an experimental feature: use it at your own risk. |
| [in] | interpPtsPerWavelength | If useInterpolation is set to true, this parameter determines the number of points per "effective wavelength" (defined as 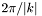 , where , where 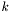 = = waveNumber) used to construct the interpolation grid. The default value (5000) is normally enough to reduce the relative or absolute error, whichever is smaller, below 100 * machine precision. If useInterpolation is set to false, this parameter is ignored. |
None of the shared pointers may be null and the spaces range and dualToRange must be defined on the same grid, otherwise an exception is thrown.
If local-mode ACA assembly is requested (see AcaOptions::mode), after discretization, the weak form of this operator is stored as the product
![\[ P A_{\textrm{d}} Q, \]](form_86.png)
where 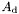 is the weak form of this operator discretized with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of
is the weak form of this operator discretized with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of domain and range to individual elements; 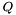 is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the basis functions of
is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the basis functions of domain in the just mentioned single-element trial functions; and 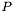 is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of
is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of dualToRange in the single-element test functions.
| BasisFunctionType | Type of the values of the basis functions into which functions acted upon by the operator are expanded. |
| KernelType | Type of the values of the kernel functions occurring in the integrand of the operator. |
| ResultType | Type used to represent elements of the weak form form of the operator. |
The latter three template parameters can take the following values: float, double, std::complex<float> and std::complex<double>. All types must have the same precision: for instance, mixing float with std::complex<double> is not allowed. The parameter ResultType is by default set to "larger" of BasisFunctionType and KernelType, e.g. for BasisFunctionType = double and KernelType = std::complex<double> it is set to std::complex<double>. You should override that only if you set both BasisFunctionType and KernelType to a real type, but you want the entries of the operator's weak form to be stored as complex numbers.
Note that setting KernelType to a real type implies that the wave number must also be chosen purely real.
References Bempp::AssemblyOptions::ACA, Bempp::AssemblyOptions::acaOptions(), Bempp::AssemblyOptions::assemblyMode(), and Bempp::AcaOptions::mode.
Referenced by Bempp::helmholtz3dAdjointDoubleLayerBoundaryOperator().
| BoundaryOperator< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dDoubleLayerBoundaryOperator | ( | const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > & | context, |
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | domain, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | range, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | dualToRange, | ||
| KernelType | waveNumber, | ||
| const std::string & | label = "", |
||
| int | symmetry = NO_SYMMETRY, |
||
| bool | useInterpolation = false, |
||
| int | interpPtsPerWavelength = DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY |
||
| ) |
Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the double-layer boundary operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D.
| [in] | context | A Context object that will be used to build the weak form of the boundary operator when necessary. |
| [in] | domain | Function space being the domain of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | range | Function space being the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | dualToRange | Function space dual to the the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | waveNumber | Wave number. See Modified Helmholtz equation in 3D for its definition. |
| [in] | label | Textual label of the operator. If empty, a unique label is generated automatically. |
| [in] | symmetry | Symmetry of the weak form of the operator. Can be any combination of the flags defined in the enumeration type Symmetry. |
| [in] | useInterpolation | If set to false (default), the standard exp() function will be used to evaluate the exponential factor occurring in the kernel. If set to true, the exponential factor will be evaluated by piecewise-cubic interpolation of values calculated in advance on a regular grid. This normally speeds up calculations, but might result in a loss of accuracy. This is an experimental feature: use it at your own risk. |
| [in] | interpPtsPerWavelength | If useInterpolation is set to true, this parameter determines the number of points per "effective wavelength" (defined as 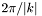 , where , where 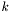 = = waveNumber) used to construct the interpolation grid. The default value (5000) is normally enough to reduce the relative or absolute error, whichever is smaller, below 100 * machine precision. If useInterpolation is set to false, this parameter is ignored. |
None of the shared pointers may be null and the spaces range and dualToRange must be defined on the same grid, otherwise an exception is thrown.
If local-mode ACA assembly is requested (see AcaOptions::mode), after discretization, the weak form of this operator is stored as the product
![\[ P A_{\textrm{d}} Q, \]](form_86.png)
where 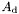 is the weak form of this operator discretized with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of
is the weak form of this operator discretized with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of domain and range to individual elements; 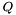 is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the basis functions of
is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the basis functions of domain in the just mentioned single-element trial functions; and 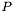 is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of
is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of dualToRange in the single-element test functions.
| BasisFunctionType | Type of the values of the basis functions into which functions acted upon by the operator are expanded. |
| KernelType | Type of the values of the kernel functions occurring in the integrand of the operator. |
| ResultType | Type used to represent elements of the weak form form of the operator. |
The latter three template parameters can take the following values: float, double, std::complex<float> and std::complex<double>. All types must have the same precision: for instance, mixing float with std::complex<double> is not allowed. The parameter ResultType is by default set to "larger" of BasisFunctionType and KernelType, e.g. for BasisFunctionType = double and KernelType = std::complex<double> it is set to std::complex<double>. You should override that only if you set both BasisFunctionType and KernelType to a real type, but you want the entries of the operator's weak form to be stored as complex numbers.
Note that setting KernelType to a real type implies that the wave number must also be chosen purely real.
References Bempp::AssemblyOptions::ACA, Bempp::AssemblyOptions::acaOptions(), Bempp::AssemblyOptions::assemblyMode(), and Bempp::AcaOptions::mode.
Referenced by Bempp::helmholtz3dDoubleLayerBoundaryOperator().
| BoundaryOperator< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dHypersingularBoundaryOperator | ( | const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > & | context, |
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | domain, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | range, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | dualToRange, | ||
| KernelType | waveNumber, | ||
| const std::string & | label = "", |
||
| int | symmetry = NO_SYMMETRY, |
||
| bool | useInterpolation = false, |
||
| int | interpPtsPerWavelength = DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY |
||
| ) |
Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the hypersingular operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D.
| [in] | context | A Context object that will be used to build the weak form of the boundary operator when necessary. |
| [in] | domain | Function space being the domain of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | range | Function space being the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | dualToRange | Function space dual to the the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | waveNumber | Wave number. See Modified Helmholtz equation in 3D for its definition. |
| [in] | label | Textual label of the operator. If empty, a unique label is generated automatically. |
| [in] | symmetry | Symmetry of the weak form of the operator. Can be any combination of the flags defined in the enumeration type Symmetry. |
| [in] | useInterpolation | If set to false (default), the standard exp() function will be used to evaluate the exponential factor occurring in the kernel. If set to true, the exponential factor will be evaluated by piecewise-cubic interpolation of values calculated in advance on a regular grid. This normally speeds up calculations, but might result in a loss of accuracy. This is an experimental feature: use it at your own risk. |
| [in] | interpPtsPerWavelength | If useInterpolation is set to true, this parameter determines the number of points per "effective wavelength" (defined as 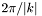 , where , where 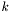 = = waveNumber) used to construct the interpolation grid. The default value (5000) is normally enough to reduce the relative or absolute error, whichever is smaller, below 100 * machine precision. If useInterpolation is set to false, this parameter is ignored. |
None of the shared pointers may be null and the spaces range and dualToRange must be defined on the same grid, otherwise an exception is thrown.
If local-mode ACA assembly is requested (see AcaOptions::mode), after discretization, the weak form of this operator is stored as the product
![\[ A = \sum_{i=1}^3 P_i A_{\textrm{d}} Q_i + k^2 \sum_{i=1}^3 R_i A_{\textrm{d}} S_i, \]](form_121.png)
where:
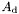 is the weak form of the single-layer modified Helmholtz boundary operator discretised with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of
is the weak form of the single-layer modified Helmholtz boundary operator discretised with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of domain and range to individual elements;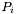 is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the
is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the 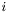 th component of the surface curl of the basis functions of
th component of the surface curl of the basis functions of dualToRange in the single-element test functions mentioned above;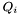 is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the
is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the 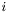 th component of the surface curl of the basis functions of
th component of the surface curl of the basis functions of domain in the single-element trial functions;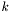 is the wave number
is the wave number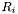 is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of
is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of dualToRange, multiplied by the 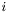 th component of the local vector normal to the surface on which functions from
th component of the local vector normal to the surface on which functions from dualToRange live, in the single-element test functions;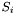 is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of basis functions of
is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of basis functions of domain, multiplied by the 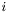 th component of the local vector normal to the surface on which functions from
th component of the local vector normal to the surface on which functions from domain live, in the single-element trial functions.| BasisFunctionType | Type of the values of the basis functions into which functions acted upon by the operator are expanded. |
| KernelType | Type of the values of the kernel functions occurring in the integrand of the operator. |
| ResultType | Type used to represent elements of the weak form form of the operator. |
The latter three template parameters can take the following values: float, double, std::complex<float> and std::complex<double>. All types must have the same precision: for instance, mixing float with std::complex<double> is not allowed. The parameter ResultType is by default set to "larger" of BasisFunctionType and KernelType, e.g. for BasisFunctionType = double and KernelType = std::complex<double> it is set to std::complex<double>. You should override that only if you set both BasisFunctionType and KernelType to a real type, but you want the entries of the operator's weak form to be stored as complex numbers.
Note that setting KernelType to a real type implies that the wave number must also be chosen purely real.
References Bempp::AssemblyOptions::ACA, Bempp::AssemblyOptions::acaOptions(), Bempp::AssemblyOptions::assemblyMode(), and Bempp::AcaOptions::mode.
Referenced by Bempp::helmholtz3dHypersingularBoundaryOperator().
| BoundaryOperator< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > Bempp::modifiedHelmholtz3dSingleLayerBoundaryOperator | ( | const shared_ptr< const Context< BasisFunctionType, ResultType > > & | context, |
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | domain, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | range, | ||
| const shared_ptr< const Space< BasisFunctionType > > & | dualToRange, | ||
| KernelType | waveNumber, | ||
| const std::string & | label = "", |
||
| int | symmetry = NO_SYMMETRY, |
||
| bool | useInterpolation = false, |
||
| int | interpPtsPerWavelength = DEFAULT_HELMHOLTZ_INTERPOLATION_DENSITY |
||
| ) |
Construct a BoundaryOperator object representing the single-layer boundary operator associated with the modified Helmholtz equation in 3D.
| [in] | context | A Context object that will be used to build the weak form of the boundary operator when necessary. |
| [in] | domain | Function space being the domain of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | range | Function space being the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | dualToRange | Function space dual to the the range of the boundary operator. |
| [in] | waveNumber | Wave number. See Modified Helmholtz equation in 3D for its definition. |
| [in] | label | Textual label of the operator. If empty, a unique label is generated automatically. |
| [in] | symmetry | Symmetry of the weak form of the operator. Can be any combination of the flags defined in the enumeration type Symmetry. |
| [in] | useInterpolation | If set to false (default), the exp() function from the standard C++ library will be used to evaluate the exponential factor occurring in the kernel. If set to true, the exponential factor will be evaluated by piecewise-cubic interpolation of values calculated in advance on a regular grid. This normally speeds up calculations, but might result in a loss of accuracy. Use at your own risk. |
| [in] | interpPtsPerWavelength | If useInterpolation is set to true, this parameter determines the number of points per "effective wavelength" (defined as 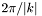 , where , where 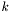 = = waveNumber) used to construct the interpolation grid. The default value (5000) should ensure that the interpolated values are accurate to about 50 * machine precision. |
None of the shared pointers may be null and the spaces range and dualToRange must be defined on the same grid, otherwise an exception is thrown.
If local-mode ACA assembly is requested (see AcaOptions::mode), after discretization, the weak form of this operator is stored as the product
![\[ P A_{\textrm{d}} Q, \]](form_86.png)
where 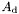 is the weak form of this operator discretized with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of
is the weak form of this operator discretized with test and trial functions being the restrictions of the basis functions of domain and range to individual elements; 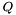 is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the basis functions of
is the sparse matrix representing the expansion of the basis functions of domain in the just mentioned single-element trial functions; and 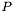 is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of
is the sparse matrix whose transpose represents the expansion of the basis functions of dualToRange in the single-element test functions.
| BasisFunctionType | Type of the values of the basis functions into which functions acted upon by the operator are expanded. |
| KernelType | Type of the values of the kernel functions occurring in the integrand of the operator. |
| ResultType | Type used to represent elements of the weak form form of the operator. |
The latter three template parameters can take the following values: float, double, std::complex<float> and std::complex<double>. All types must have the same precision: for instance, mixing float with std::complex<double> is not allowed. The parameter ResultType is by default set to "larger" of BasisFunctionType and KernelType, e.g. for BasisFunctionType = double and KernelType = std::complex<double> it is set to std::complex<double>. You should override that only if you set both BasisFunctionType and KernelType to a real type, but you want the entries of the operator's weak form to be stored as complex numbers.
Note that setting KernelType to a real type implies that the wave number must also be chosen purely real.
References Bempp::AssemblyOptions::ACA, Bempp::AssemblyOptions::acaOptions(), Bempp::AssemblyOptions::assemblyMode(), and Bempp::AcaOptions::mode.
Referenced by Bempp::helmholtz3dSingleLayerBoundaryOperator().
 1.8.5
1.8.5